So you've also heard about Web3. Bravo! You're officially a nerd. Haha, just kidding.
Techies everywhere, especially on Twitter, frequently use the term "web3". And it’s my job as the web3 "Shinobi" to simplify and explain its geeky concepts in the most basic way possible.
The Web3 concept is not new; it has existed for some time, but it has only recently gained popularity.
To be clear, you don't have to be a techie to understand what web3 is. Its existence has an impact on each of us, whether positively or negatively. Okay, enough with the chit-chat; let's get down to business.
Let's travel back in time

Over the last few years, there have been three versions of the web: web1, web2, and web3. In this article, we'll look at what each of these web versions is, when they were created, and how they differ from one another.
What is Web 1.0?
Tim-Bernes Lee came up with the term "web1" in 1989, and it’s known as the initialization stage of the internet. According to Tim, the internet wasthe "Read-only Web". This was because people could only consume/read content and not create it.
Instead of websites with content that could change over time, Web1 sites served static HTML content from a static file system rather than a database, and users could not interact with web pages in any way.
The majority of these websites were informative. Businesses used their websites to advertise their goods and services. There were also personal websites where users could show off their photos, list all their Pokémon collections, and upload weird photos of Arnold Schwazenegger

Websites were not visited multiple times because the content was often the same and would remain that way for years, if not the entire lifetime of the website, as long as it was running on the web1 architecture.
Web1.0 lasted roughly from 1991 to 2004
Main characteristics of web1
- Static web pages
- Content served from the file system
- Banner advertising
- Pages built using Server Side Includes or Common Gateway Interface (CGI).
- Mostly read-only
What is Web 2.0?
If you're reading this article on this platform and have a Google or Facebook account, you're probably familiar with "web2," as it's what most modern platforms run on.
Unlike web1, this version of the web has evolved to be more social, participative, and interactive. We can express ourselves and share our ideas. Our ability to upload cat videos and photos of ourselves to platforms like Facebook and Snapchat allows us to generate our own content. We can engage with other content by liking, sharing, and commenting on them, among other things. People have made a lot of money by posting videos of themselves doing stuff they regularly do, like dancing, playing games, and so on.
For content creators, the Internet is now a gold mine.
Main characteristics of web2
- User interaction & participation
- Rich user interface and experience
- Dynamic content
- Contains collective intelligence by way of user engagement.
Big Tech dominates this version of the world wide web: Facebook, Google, Amazon, Instagram, TikTok, and all of the other tech and social platforms we know and love today. These platforms have a centralized structure that allows them to generate revenue to operate their businesses and pay their employees.
On Web2, you have no control over your data, nor do you have any say over where or how it is stored. These platforms collect and profit from your data (often without your permission) by selling it to advertisers. The saddest part is that we freely trade our information when we sign up on these platforms. And the more data they collect about us, the more money they make from advertising sales. Do we get a share of that money? Nope, we don't. Instead, we are shown more personalized content coupled with extremely annoying ads in our feed.

Problems with web2
Privacy. Our activity on web2 platforms is frequently monitored. Our searches, clicks, videos watched, location, names, and other personal information are all recorded. These platforms know us even more than we know ourselves. Think of the consequences if this information falls into the wrong hands.
Security issues. Hackers target specific data centers that contain our sensitive information. And we occasionally hear about these attacks, which result in data leaks.
Centralization. The entire system is under the control of a single authority, which can simply shut down the system or do whatever they want with it, with no one having a voice in the decision.
Censorship. Because web2 platforms are centralized, platform administrators can choose to censor or hide content as they see fit. This can sometimes hide the truth, resulting in an autocratic system rather than a democratic environment.
What is Web 3.0?
Web3, coined by Ethereum co-founder Gavin Wood in 2014, is a more evolved internet based on the concept of decentralization, a version of the web in which people own and control their data and all central entities/authorities are eliminated.
Web2 platforms are typically deployed to a server, and data is kept in a central database managed by a single cloud service provider (like AWS). As a result, anyone with access to this server or database can modify, add, or remove the information saved.
But for web3 applications or dApps(decentralized apps), data saved on the network is copied and distributed in a decentralized peer-to-peer network of thousands of nodes/computers that communicate with each other under a consensus protocol. Therefore, data cannot be deleted or modified. The only way to 'hack' or 'cheat' the system to execute this data modification is by accessing all thousands of computers and deleting/modifying specific data on every one of them, which I ensure is almost impossible.
Furthermore, web3 platforms allow full user participation without monetizing user information.
Characteristics of web3
Decentralized. This means that no single authority influences decisions that impact the entire system. Rather, it is built on a distributed peer-to-peer network of computers.
User anonymity and privacy. Personal information such as names and email addresses are not required. You only need your wallet address. Then, BOOM! you're connected.
Fast transactions without compromising security. Transactions are completed in a matter of seconds because there are no middleman services. Everything happens directly between the involved participants.
Censorship resistance. Platforms on web3 are unable to censor, modify, or remove user content because they do not have control over it.
Self-governing
- Distributed
For the characteristics mentioned above to be made possible, web3 utilizes blockchain technology and cryptography which is the ideal approach in this scenario. Let's have a look at blockchain and some other web3 terminologies:
Blockchain

Blockchain is a collection of records known as blocks that store data openly and chronologically in such a way that altering, hacking, or cheating is difficult and nearly impossible.
In its technical form, blockchain is a peer-to-peer network of nodes/computers. When data is saved to the network, copies of that data are distributed to all network nodes. So even if one node or data on one of the participant computers becomes corrupted, the other participants will be notified quickly and will be able to solve the problem as soon as possible. Now hack that if you can!
Characteristics of Blockchain
Permissionless. The system is public and participants do not need specific permissions to participate in validating and mining transactions sometimes using a mining pool.
Trustless. Participants involved do not need to know or trust each other for the system to function.
Faster transactions. Because transactions are carried out across a peer-to-peer network, there is no need for intermediary services that cause transaction delays.
Immutability. Data stored on the blockchain cannot be changed or removed
Decentralized. Every user is in control. In this system, there is no single authority.
Open and transparent. All transactions carried out on the network are stored inside a public ledger
Distributed Ledgers. A distributed ledger is a database that is shared and synchronized by multiple people across multiple sites, organizations, or geographic regions.
Smart Contracts
They are computer programs that are stored on the blockchain and only run when predetermined conditions are met. You can think of smart contracts as a real-life contract/agreement between two people.
Smart contracts are mostly written in the Solidity language.
Cryptography
Is the process of converting raw data or text into a more secure, unreadable, and encrypted format (ciphertext) using an algorithm.
Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency is a digital currency that works as a medium of exchange in a decentralized network and utilizes the concept of cryptography. Cryptocurrencies can be used without the involvement of intermediaries, such as banks or governments.
Some examples of cryptocurrencies are:
- Bitcoin
- Ethereum
- Litecoin
- Binance coin
- Polkadot
- Dogecoin
Web3 more than crypto
Web3 is not just about crypto. The reality is that crypto is only a piece of the puzzle. Web3 combines blockchain technology and crypto because its mission is to create an internet where users are in control of their data and where openness and transparency are guaranteed. Cryptocurrencies/digital currencies, on the other hand, are required when participating in activities, making purchases/investments, and contributing to projects, among other things.
So, in a nutshell, crypto and blockchain are the pillars of web3.
What are some applications of Web3?

We now have a basic understanding of what the various versions of the web are, their origins, and their main characteristics.
With decentralization as the foundation of web3, the emergence of blockchain technology, cryptography, automated smart contracts, and censorship resistance, web3 has several real-life applications. Let's look at a few :
- Finance
- Companies & Organizations
- Proof of authenticity/ownership
- 3D Interactive Technology (Metaverses)
Finance
Finance is a broad term that encompasses the creation of money, investment, money management, and everything else involving money. Traditional finance, as we know it, is centered around:
- Trading
- Payment
- Credits & Loans
- Capital markets
- Investments
- Savings and so on
All of these things make our lives easier. But this, however, has its disadvantages:
Problems with traditional financial systems
- Slow processes due to middleman services
- High commission and fees
- Strict regulations
- It takes longer to open an account.
- Filling out insanely long paperwork
- Restriction to specific countries
- Earning less interest on savings, etc
Some of these concerns relating to traditional financial institutions are solved by Web3 through Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a term that refers to a financial system built on public decentralized infrastructure. Unlike the traditional financial system, which is based on a centralized platform managed by government agencies and other intermediaries, DeFi platforms are based on blockchain and cryptocurrencies
Problems DeFi solves
- Send money anywhere with no restrictions
- Eliminates middlemen
- It is fast and instant
- No need to fill out forms to create an account
- It is completely transparent
One question I repeatedly hear on the internet is, "Will DeFi replace traditional finance?" Before we answer that, let's have a look at these statistics.
Almost 90 billion USD has already been deposited into Ethereum-based DeFi platforms. There are also reports that DeFi's growth on the Ethereum blockchain is up 780% in 2021.
Based on these figures, we may conclude that DeFi is going to the moon. However, it is unlikely that it will completely replace traditional banking.
You can also check out my Twitter thread on DeFi :)
Companies & Organizations
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is a community of individuals who are bound by rules and regulations written in computer code (smart contracts) and maintained on the blockchain. The rules and governance of the organization cannot be changed unless voted upon by the DAO’s members.
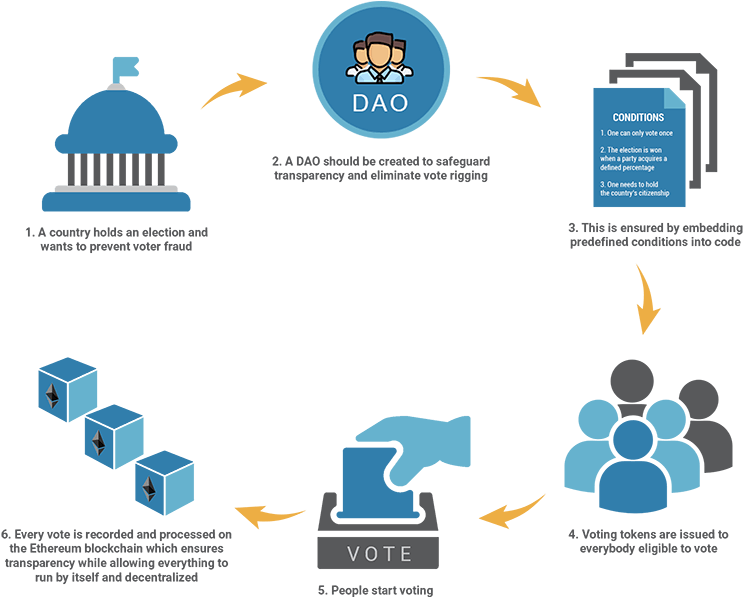
Anyone who wants to be a stakeholder in a DAO, participate in decision making (by voting), or prove their engagement with the DAO must own the DAO's official token.
LinksDAO, one of the most popular DAOs, is a blockchain-based country club for golf enthusiasts worldwide They recently launched a collection containing 9,090 NFTs, and guess what, they generated 10.4 million USD in sales in 48 hours. Crazy huh?!
Examples of DAOs
- Uniswap
- LinksDAO
- Aave
- Gitcoin
- MetaCartel Ventures
Proof of authenticity/ownership
Through Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), users can prove ownership of digital items. How does it work?
Consider the following situation. The value of a dollar remains unchanged from one dollar to the next. One dollar can be exchanged for another dollar, two dollars for another two dollars, three dollars for another three dollars, and so on.
NFTs are a sort of cryptocurrency on the Ethereum blockchain that works similarly to money. However, unlike the dollar, the value of an NFT varies from one to the next. This is because each NFT has its unique metadata.
Because the blockchain verifies each NFT's authenticity, its metadata and ownership details cannot be modified. Ever! So once you buy an NFT, you claim full ownership of that digital asset, and no one can take it away from you unless you sign a transaction that transfers ownership of the asset to someone else.
3D Interactive Technology (Metaverses)

The Metaverse is the concept of a virtual 3D universe in which users are free to do whatever they wish, just like in the real world. These Metaverses can be visited via virtual and augmented reality headsets. If you've seen movies like Ready Player One, Free Guy, Virtual Revolution, or Ghost In A Shell, you'll have a good idea of how metaverses work.
Oh, I almost forgot to mention that Facebook has changed its name to Meta, and I believe they did this to kind of 'own' the Metaverse theory (that's my opinion). And in case you didn't know, the term 'metaverse' was coined by a science fiction writer, Stephenson, in his popular 1994 novel Snow Crash.
Some platforms allow you to access virtual worlds directly from your browser. A few of them are:
- Decentraland
- Sandbox
- Somnium
How Identity Works in Web3
When signing up on a web2 platform like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter, we are required to provide our:
- Fullname
- Email address
- Age
- Location
- Profile photos
- Your interests, etc
This information is gathered and saved in the platform's database. But on a web3/blockchain-based platform, the only information required is your wallet address which you can get from creating a crypto wallet on Coinbase or Metamask. That's it! This address represents your identity on the platform and is not associated with your real identity.
There’s no need for usernames, emails, or other sensitive information. As a result, you can remain anonymous while maintaining full control over your data and content.
How do we benefit from web3?
Now that we've demystified web3 and all of its nerdy concepts, let's look at how we can benefit from it:
- We stay anonymous
- Platforms will not monetize our data
- Our content will not be taken down by any platform
- We have the freedom to start or join any project we choose
- We can send and receive funds no matter our geographic region
How to Build on Web3
Apps built on web3 are called dApps (decentralized apps).
dApps are created using standard web development languages and tools like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The only difference is that to read from and interact with the blockchain (Ethereum), you'll need a few additional languages and frameworks:
What you'll need to build dApps
- Solidity language
- Any frontend framework
- Truffle or Remix IDE
- MetaMask extension
- Web3.js, Ethers.js (JavaScript) or Web3py (Python)
Solidity
Solidity is an object-oriented programming language that is used to create and interact with Smart Contracts on the blockchain.
Frontend framework
You can choose among React, Vue, Angular, and other web frontend frameworks. My personal favorite, which I will always suggest, is React.
Truffle or Remix IDE
Truffle allows you to compile, migrate and deploy Smart Contracts. Truffle is now one of the most extensively used Ethereum Blockchain frameworks.
The Remix IDE is a smart contract editor that allows you to write, test, debug, and deploy smart contracts. If you're a beginner, I'd recommend the Remix IDE to the truffle framework. Plugins can be installed with Remix, making smart contract development easier.
MetaMask
MetaMask is a browser extension and mobile app that also functions as a cryptocurrency wallet and allows you to interact with the Ethereum network and decentralized applications (dApps).
Web3.js/Ethers.js, Web3py
Both Web3.js and Ethers.js are JavaScript libraries that allow you to interact with smart contracts from the browser.
Web3py, on the other hand, has the same features but is designed specifically for Python developers.
Conclusion
If you want to get started with web3 development, check out my article where I show you how to get started even if you're a beginner.
Also, make sure to check out Hashnode's Web3 blog to learn more about other topics in this space.
Thanks for reading 😇

